Description
Download a preview <<HERE>>
This 100% digital grammar bundle has everything you need to implement Mentor Sentences in your middle School ELA classroom, by using sentences from popular middle-grade and young adult novels.
-
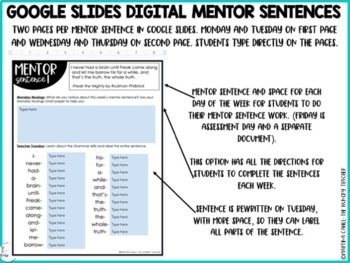
Google Slides Interactive Mentor Sentences for students to type into.
-
Google Slides Interactive Tuesday Grammar Lesson note pages for students to type right into
-
Google Forms SELF-GRADING Friday Assessments
-
Google Slides Mentor Sentences to Display
-
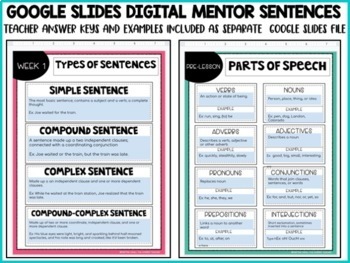
Google Slides Mentor Sentences Answer Keys for Teachers
-
Google Slides Tuesday Lesson Examples and Answers for Teachers.
-
Student grammar, parts of speech, punctuation, etc. reference sheets (8 reference pages in all). Color and black and white options. (PDF)
The first 9 weeks’ mentor texts:
-
Call of the Wild by Jack London
-
Freak the Mighty by Rodman Philbrick
-
HP Book One by J.K. Rowling
-
Percy Jackson and the Lightning Thief by Rick Riordan
-
The Absolute True Diary of a Part-Time Indian by Sherman Alexie
-
The Fault in our Stars by John Green
-
The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins
-
The Maze Runner by James Dashner
-
The Outsiders by S.E. Hinton
-
A Separate Peace by John Knowles
-
All American Boys by Jason Reynolds
-
Divergent by Veronica Roth
-
Noggin by John Corey Whaley
-
The Bad Beginning by Lemony Snicket
-
The Giver by Lois Lowry
-
The Hate U Give by Angie Thomas
-
To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee
-
White Fang by Jack London
-
A Wrinkle in Time by Madeleine L’Engle
-
Everything Everything by Nicola Yoon
-
Matched by Ally Condie
-
Me, Earl and the Dying Girl by Jesse Andrews
-
Middle School- The Worst Years of My Life by James Patterson
-
Miss Peregrine’s Home for Peculiar Children by Ransom Riggs
-
Schooled by Gordon Korman
-
The Hobbit by J.R.R Tolkien
-
Thirteen Reasons Why by Jay Asher
-
Booked by Kwame Alexander
-
Miss Peregrine’s Home for Peculiar Children by Ransom Riggs
-
Orbiting Jupiter by Gary Schmidt
-
Red Queen by Victoria Aveyard
-
Simon vs. the Homo Sapiens Agenda
-
The Book Thief by Markus Zusak
-
The Crossover by Kwame Alexander
-
The Perks of Being a Wallflower by Stephen Chbosky
-
Where the Mountain Meets the Moon by Grace Lin
-
Parts of Speech
-
Simple Sentences, Complex, Compound, and Compound-Complex
-
Independent and Dependent Clauses
-
Figurative Language: Hyperboles
-
Types of Phrases: Absolute, Appositive, Gerund, Infinite, Noun, Participle, and Prepositional
-
Colons and Semicolons
-
Types of Pronouns: Possessive, Reflexive, Reciprocal, Demonstrative, Interrogative, and Indefinite
-
Subordinating and Coordinating Conjunctions
-
Using Quotation Marks Correctly
-
Verb Moods: Indicative, Imperative, Interrogative, Conditional, and Subjunctive
-
Figurative Language: Personification
-
Common Prefixes and their Meanings
-
Using Context Clues to determine word meanings
-
Connotation and Denotation
-
Verbs: Infinitive, Present Participle, Past Participle, and Past Tense
-
Common and Proper Nouns
-
Common Homophones
-
Intensive and Vague Pronouns
-
Direct and Indirect Objects
-
Object of the Preposition
-
Figurative Language: Metaphor and Simile
-
Punctuation Nonrestrictive Elements
-
Author Style and Tone
-
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
-
Benefits of using the four different types of sentence structure (variety)
-
Proper Noun Rules
-
Dangling Modifier Rules
-
Expressing Ideas Precisely and eliminating wordiness and redundancy
-
Plural Noun Rules
-
Verbals, Gerunds, and Infinitives
-
Past and Present Participle
-
Abstract Nouns
-
Concrete Nouns
-
Punctuating and Capitalizing Titles of Works
-
Subjects and Predicates
-
Simple Subjects and Predicates
-
Compound Subjects and Predicates
-
Verb Tenses (12 Different Verb Tenses)
-
Verbs: Action, Helping, and Linking
-
Figurative Language: Allusion
-
Rules for Using Numbers in English
-
Rules for Using Apostrophes in English
-
Rules for Using Commas in English
-
Prepositions and Prepositional Phrases
-
Direct and Indirect Objects
-
Object of the Preposition
-
Commonly Confused Words
-
Irony: Situational, Dramatic, and Verbal
-
Active and Passive Verbs
-
Sentences: Imperative, Exclamatory, Interrogative, and Declarative
-
Adjectives: Descriptive, Quantitative, Demonstrative, Possessive, Distributive, Interrogative, and Articles
-
Antonyms and Synonyms
-
Figurative Language: Idioms
-
Differences between Who and Whom
-
Middle School Mentor Sentences Volume 1: Two Free Weeks
-
Middle School Mentor Sentences Volume 2: Two Free Weeks